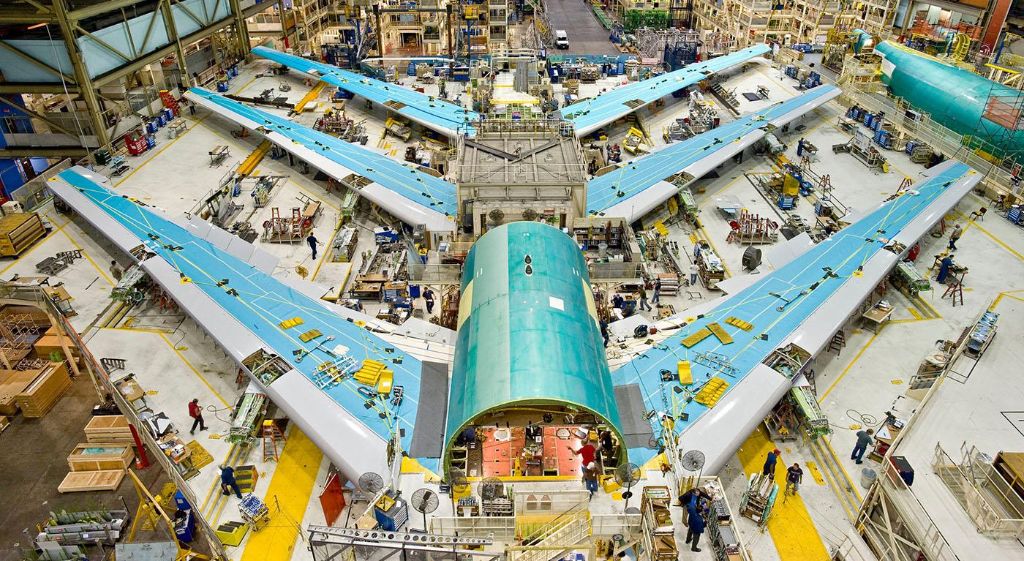
The Aerospace sector is a vibrant, high value, high technology engineering, manufacturing and service industry - with strengths are in areas such as the design and manufacture of large aircraft wings; aircraft engines; helicopters and advanced systems including landing gear, fuel, mechanical, avionics and electrical power.
The aerospace sector is well placed to take advantage of the increased demand for air travel and rising demand for new aircraft as a result of rising per capita income.
Environmental regulations and considerations are key drivers for the latest technology developments.
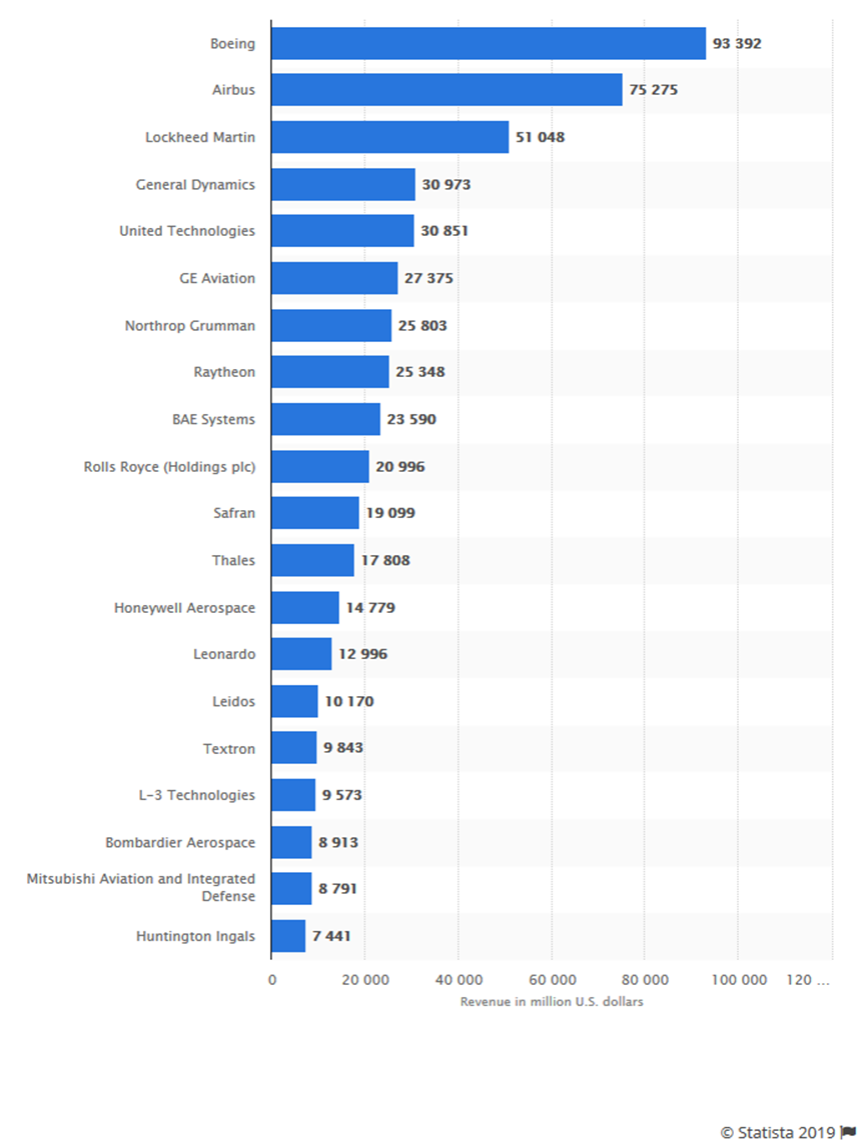
The sector has significant economies of scale and is therefore highly concentrated. It is, however, open to international competition and strong global brands are important. Airbus, Rolls Royce and Bombardier are key players in the global market.
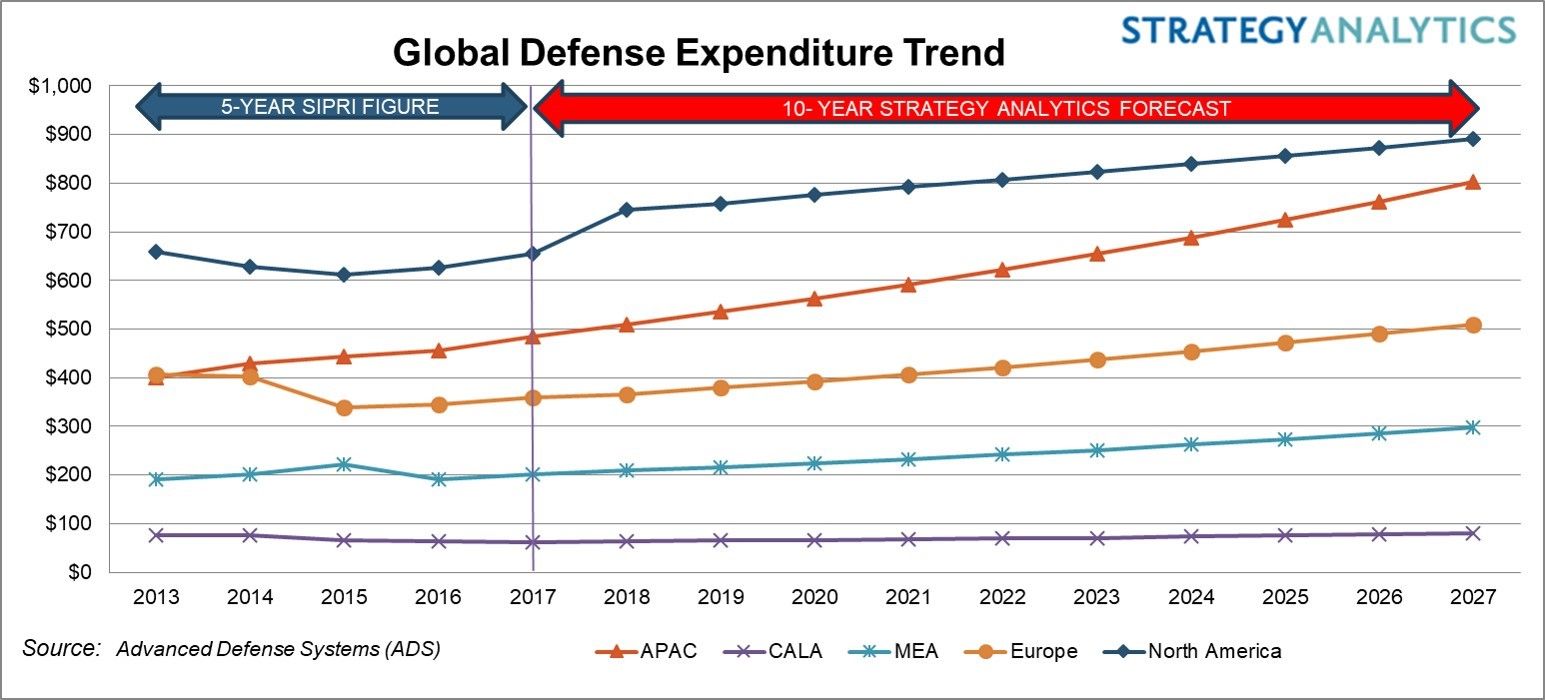
UK has a 17% global market share in aerospace industry revenues: the largest in Europe and second only to the US worldwide. Furthermore the sector supports more than 3,000 companies distributed across the UK, directly employing 100,000 people and supporting an additional 130,000 jobs indirectly. Finally, it has been estimated that there will be global demand for 27,000 new passenger aircraft, worth around .7 trillion, by 2031. In addition, global demand for commercial helicopters is expected to be in excess of 40,000 and worth circa 5 billion by 2031.
With fuel prices being volatile, optimizing resources is a priority for the aerospace sector.
Research and development plays a key role in Aerospace Industry to meet the changing needs and requirements. The aerospace industry is engaged in researching, designing, manufacturing and operating commercial, industrial and military aircrafts. Besides, the defense sector, spacecrafts open up opportunities for the introduction of emerging technologies.
The added pressure to reduce emissions, is driving the need for innovation to reduce component weight.
The industry is witnessing a great transformation driven by increasing awareness in green power, as well as advances in nanotechnology and smart materials, which are lightweight yet robust enabling better aerodynamics and passenger safety.