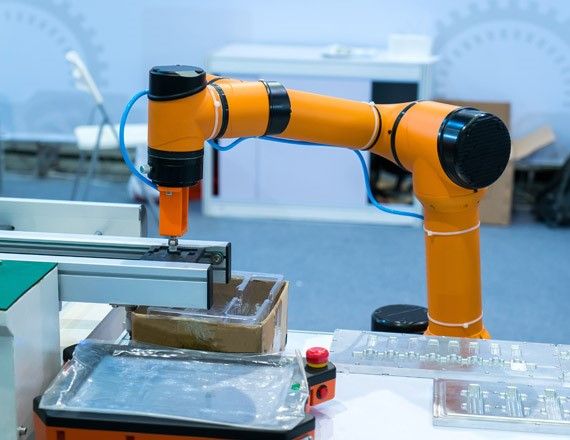
The increasing emphasis on industrial automation and optimum utilization of resources, is driving the industry control and factory automation market, encompassing industrial robots, sensors, field instruments, machine vision, control valves, HMI, industrial PC, and industrial 3D printing.
Robotics is fast emerging, covering industrial robotics, service robotics, medical robotics, surgical robotics, personal robotics, and home care robots.
Big data and analytics, along with industrial internet of things (IoT), are expected to further revolutionize automation.
Manufacturers are leveraging the potential of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, big data and machine learning, and additive manufacturing techniques, to accelerate the process of bringing innovation to market, and make their production processes more intelligent and responsive to emerging consumer needs.
According to IDC, by the End of 2021, 25% of Global Manufacturers will Apply Machine Learning to Data Across Product Development, Supply Chain, Manufacturing, and Service for More Rapid Decision Support, Improved Quality, Differentiated Products, and Innovative Business Models.
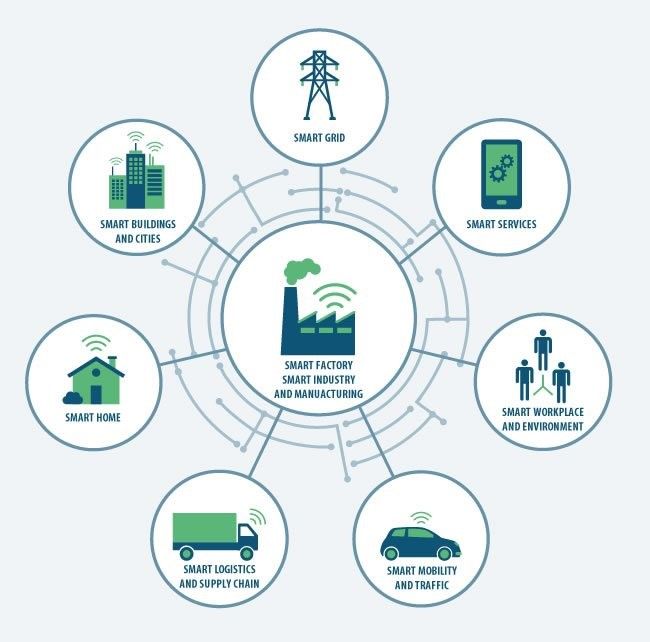
Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 smart manufacturing and industrial IoT, enable manufactures to enhance existing production capabilities in aligning the innovation process with market demands and developing the next generation of resilient, lean production capabilities.
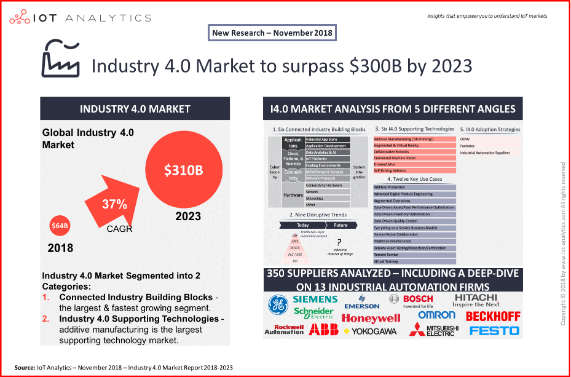
The adoption of Industry 4.0, as well as the advancements in machine-to-machine learning protocols and the adoption of better industrial interconnect standards, encompassing the smart factory environment, seem to lead the way in next generation factory automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies, led by advancements in sensors and by integrating real-time operational intelligence in supply chains via artificial neural networks.
Areas benefitting from developments in factory automation include the automotive, semiconductors and electronics, food and beverages, packaging and pharmaceutical industries.
Networking Technologies & Digital Platforms
According to IDC by 2022, 25% of manufacturers will be engaged in cross-industry collaboration, resulting in a 10% revenue increase.
Alongside the growing applications of industrial IoT to connect industrial devices, the integration between IT systems and factory installations and the need for high performance will boost the growth of the Networking technologies, such as wireless and industrial Ethernet.
According to IDC, by 2020, 60% of manufacturers will rely on digital platforms that enhance their investments in ecosystems, experiences and support as much as 30% of their overall revenue.
Supply Chain 4.0
Supply Chain 4.0 - the application of the Internet of Things, robotics, and advanced analytics of big data in supply chain management: place sensors in everything, create networks everywhere, automate anything, and analyze everything to significantly improve performance and customer satisfaction - will impact all areas in supply chain management.
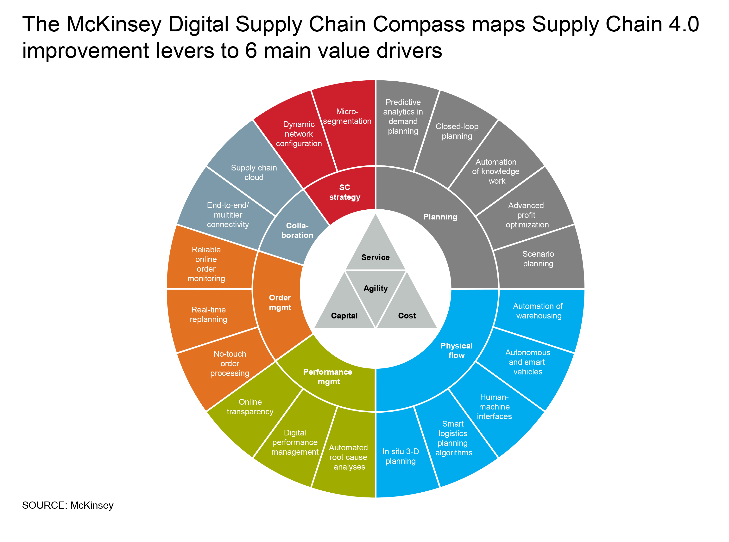
Digital Supply Chain: According to IDC, by the end of 2020, one-third of all manufacturing supply chains will be using analytics-driven cognitive capabilities in integrating products and services and increasing digital engagement, thus increasing cost efficiency by 10% and service performance by 5%.
Controls, Sensors & Robotic automation
The growing importance of the industrial Internet of Things, Robotic automation and Sensors have redefined manufacturing processes and production.
Smart sensors are used with instrumentation devices with applications in the electronics, communication, and industrial automation industries. Emerging communication technologies such as satellite-based personal networks, and advanced wireless communication technologies such as wireless internet and LAN, are expected to boost the demand of sensors and instruments. The new entrants in the market can gain ground by focusing on. Emerging economies such as China and India are expected to offer the most lucrative sensors markets.
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and robotic automation, are enhancing the prospects in the controls markets.
The advancement of the industrial Internet of Things (IoT), and the increasing adoption of smart grids will drive further demand for factory automation sensors.
The automotive sector will accelerate this market’s growth due to the implementation of regulatory standards for commercial and passenger vehicles.
Electrical systems and components
Electrical systems and components include devices such as switch gears, controls, cables, and circuit breakers, with application in electric systems such as micro-grids and digital substations to eliminate transmission inefficiencies and facilitate the optimum deployment of existing electric power systems.
The Instrumentation market
The instrumentation industry being critical to factory automation has enabled high output with minimum to no defective pieces through proactive solutions to analyze, measure and monitor the performance level of products will encounter sustained growth.
The Drives market
As energy efficiency regulations are calling for energy optimization and efficiency, reduction in operational costs, as well as rising industrialization and urbanization will boost the growth of the drives market - such as alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) -- is anticipated to grow in near future.
Testing, Inspection and Certification
The testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) services ensure that a product meets the regulatory standards related to quality, technical safety, and performance. The implementation of new regulations & standards to ensure quality & safety are major drivers for the growth of the market.
Major players operating in the industrial control and factory automation market are ABB (Switzerland), Siemens (Germany), General Electric (US), Emerson (US), Schneider (France), Yokogawa (Japan), Endress+Hauser (Switzerland), Honeywell (US), WIKA (Germany), Azbil (Japan), Fuji Electric (Japan), Mitsubishi Electric (Japan), Omron (Japan), Yokogawa (Japan), Fanuc (Japan), Hitachi (Japan), Yaskawa (Japan), 3D Systems (US), HP (US), Vega (Germany), Danfoss (Denmark), Tegan Innovations (Ireland), Krohne (Germany), Rockwell (US), Chaos Prime (US), and Dwyer (US), STRATASYS (US), Progea (Italy).



 Manufacturing and Engineering
Manufacturing and Engineering