Social media market trends for brand awareness
Dr. Evangelo Damigos; PhD | Head of Digital Futures Research Desk
- Competitive Differentiation
Publication | Update: Oct 2022

Once a company has discovered its brand, it is important to build brand awareness. Brand awareness is the extent to which consumers or the public are familiar with a company, its distinctive features and the products or services it offers. It helps potential customers distinguish the product from the competition and can be crucial when launching a new product or service.[1]
Social media is one of the most reliable and widely used sources of user-generated product and brand reviews. Social media is an important marketing tool to understand the needs of customers as it provides access to a large number of people in one place. They offer a company the opportunity to be seen by a growing number of people and allow it to connect with customers in the best possible way and positively influence its brand, which is one of the main goals of social marketers.
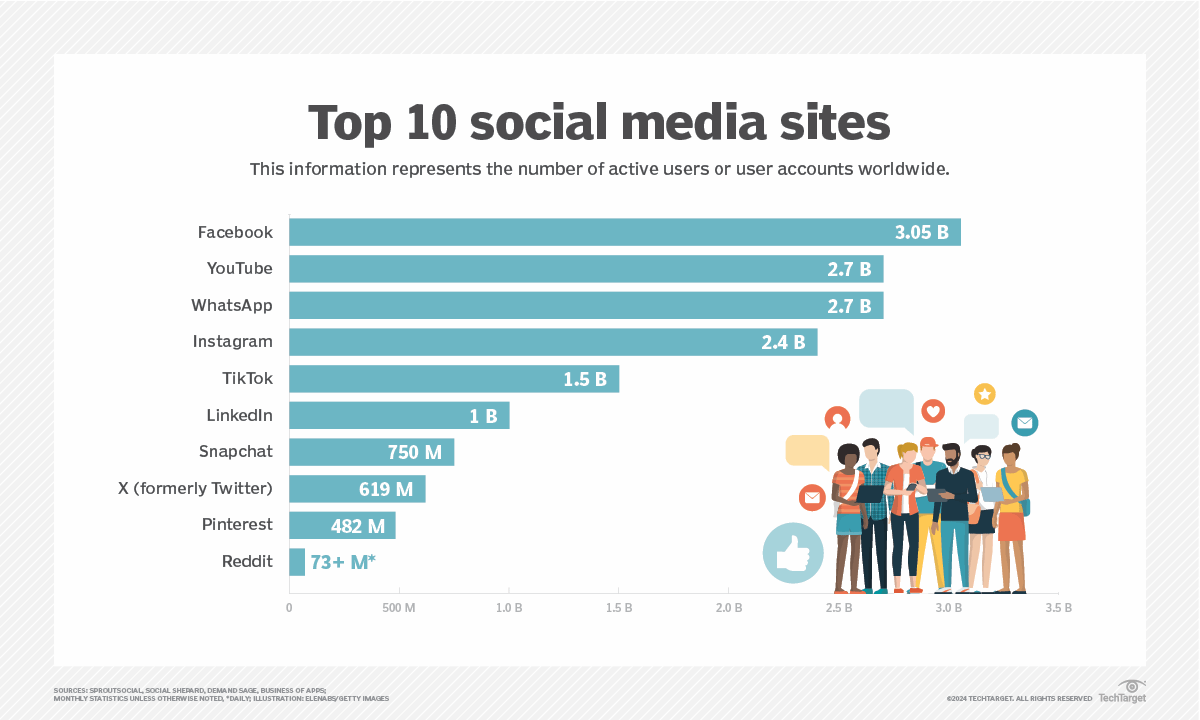
Figure 1: Top 10 social media sites. Hetler, A. (2022, June). 9 social media trends in 2022. TechTarget. Retrieved from: https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/feature/9-social-media-trends
Figure 2: Social marketer’s biggest goals. Ecomet360. (2022, July). How social media helps in increasing brand awareness - 2022 guide. LinkedIn. Retrieved from: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/how-social-media-helps-increasing-brand-awareness-2022-?trk=pulse-article_more-articles_related-content-card
Keeping up with the latest trends in social media and marketing can help a business stand out from the crowd and attract customers in a world dominated by digital content. Here are the most important social media trends for 2022.
· TikTok will become bigger
TikTok recorded more than one billion active monthly users in September 2021 and continues to expand. This is a must-have for businesses looking to target younger consumers and one of the most important channels to reach Gen Z and Millennials. It is also a suitable place for businesses to advertise with short videos that are popular among younger generations. In addition, TikTok's platform is enhanced with advertising and business profile features.
· Augmented reality will go mainstream
Other technologies such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are being integrated into social media to increase customer engagement. AR is used to enhance graphics shared on Instagram and Snapchat, although VR is still in its infancy. Snapchat, for example, applies AR for all its photo filters to turn people into animals, make them look like they are wearing cosmetics or sunglasses, and make other adjustments to their appearance. This technology can be used for more than just photo filters. People can try things out before they buy them, such as digitally placing furniture in a room or trying on sunglasses.[2]
· Interact with Followers
Social media is called that for a reason. A brand should initiate interactions with its followers and post information that encourages them to comment. This way, it will attract additional followers and retain the ones it already has. It will also make it easy for them to remember the brand when they have similar needs.
· Use Hashtags
Posts that contain at least one hashtag receive about 12.6 percent more engagement than posts without a hashtag. For instance, Instagram users can search for photos and profiles using hashtags. So, if a company wants to improve its brand awareness there, it needs to start using hashtags.[3]
· Create visual content
For a company's content to stand out in the crowded world of social media, it must include graphics and videos. It should come as no surprise that social media is a major use case for marketers creating and posting visual content. Fortunately, not every post needs to be accompanied by hand-drawn images. Royalty-free stock photos (e.g., from Adobe) and GIFs can add a simple visual element to a post, while Canva and Biteable allow the creation of custom images and video content.[4]
· Collaborate With Niche Influencers
Influencers are social media content creators with a significant number of followers. Working with niche influencers can be extremely beneficial to a company's brand, as it can increase brand awareness among its followers. Take Alfie Deyes, who has 4.4 million Instagram followers, as an example. He has worked with Daniel Wellington to market the company's watches. As an influencer, Alfie Deyes, whose Instagram account is called 'Pointless Blog', has an unprecedented pool of followers, largely influenced by his clothing and aesthetic. Through this collaboration, Daniel Wellington has been able to reach a large audience and establish the brand’s reputation.
A brand can develop a variety of content with social media influencers across multiple channels. It can ask them to manage its Instagram account or Facebook page. Given the credibility they have built with their audience, product reviews from influencers can have a positive effect on a company's brand. If a business wants to head hunt and collaborate with influencers, they can use Unbox Social's Influencer Suite. This influencer marketing tool not only helps identify brand-related influencers, but also manages and monitors influencer campaigns. There are numerous ways a company can leverage its influencers’ network to generate buzz around its brand on social media platforms.[5]
[1] Pivotal New Media. (2021, October). Can social media marketing increase brand awareness? Retrieved from: https://pivotalnewmedia.com/pivotal-thoughts/can-social-media-marketing-increase-brand-awareness/
[2] Hetler, A. (2022, June). 9 social media trends in 2022. TechTarget. Retrieved from: https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/feature/9-social-media-trends
[3] Okugbe, O. (2022, September). 31 practical ways to increase brand awareness with social media. Adoric Technologies LTD. Retrieved from: https://adoric.com/blog/brand-awareness-social-media/
[4] Branigan, S. (2021, August). 10 tips for increasing brand awareness with social media marketing. Blend Marketing Ltd. Retrieved from: https://www.blendb2b.com/blog/10-tips-for-increasing-brand-awareness-with-social-media-marketing
[5] Unbox Social. (2022, May). How to build brand awareness on social media. Retrieved from: https://www.unboxsocial.com/blog/social-media-brand-awareness/
 Digital Themes: Competitive Differentiation
Digital Themes: Competitive Differentiation

HTML
 Access Rights | Content Availability:
Access Rights | Content Availability: 


Objectives and Study Scope
This study has assimilated knowledge and insight from business and subject-matter experts, and from a broad spectrum of market initiatives. Building on this research, the objectives of this market research report is to provide actionable intelligence on opportunities alongside the market size of various segments, as well as fact-based information on key factors influencing the market- growth drivers, industry-specific challenges and other critical issues in terms of detailed analysis and impact.
The report in its entirety provides a comprehensive overview of the current global condition, as well as notable opportunities and challenges.
The analysis reflects market size, latest trends, growth drivers, threats, opportunities, as well as key market segments. The study addresses market dynamics in several geographic segments along with market analysis for the current market environment and future scenario over the forecast period.
The report also segments the market into various categories based on the product, end user, application, type, and region.
The report also studies various growth drivers and restraints impacting the market, plus a comprehensive market and vendor landscape in addition to a SWOT analysis of the key players.
This analysis also examines the competitive landscape within each market. Market factors are assessed by examining barriers to entry and market opportunities. Strategies adopted by key players including recent developments, new product launches, merger and acquisitions, and other insightful updates are provided.
Research Process & Methodology
We leverage extensive primary research, our contact database, knowledge of companies and industry relationships, patent and academic journal searches, and Institutes and University associate links to frame a strong visibility in the markets and technologies we cover.
We draw on available data sources and methods to profile developments. We use computerised data mining methods and analytical techniques, including cluster and regression modelling, to identify patterns from publicly available online information on enterprise web sites.
Historical, qualitative and quantitative information is obtained principally from confidential and proprietary sources, professional network, annual reports, investor relationship presentations, and expert interviews, about key factors, such as recent trends in industry performance and identify factors underlying those trends - drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges influencing the growth of the market, for both, the supply and demand sides.
In addition to our own desk research, various secondary sources, such as Hoovers, Dun & Bradstreet, Bloomberg BusinessWeek, Statista, are referred to identify key players in the industry, supply chain and market size, percentage shares, splits, and breakdowns into segments and subsegments with respect to individual growth trends, prospects, and contribution to the total market.
Research Portfolio Sources:
Global Business Reviews, Research Papers, Commentary & Strategy Reports
M&A and Risk Management | Regulation

The future outlook “forecast” is based on a set of statistical methods such as regression analysis, industry specific drivers as well as analyst evaluations, as well as analysis of the trends that influence economic outcomes and business decision making.
The Global Economic Model is covering the political environment, the macroeconomic environment, market opportunities, policy towards free enterprise and competition, policy towards foreign investment, foreign trade and exchange controls, taxes,
financing, the labour market and infrastructure.
We aim update our market forecast to include the latest market developments and trends.
Review of independent forecasts for the main macroeconomic variables by the following organizations provide a holistic overview of the range of alternative opinions:
As a result, the reported forecasts derive from different forecasters and may not represent the view of any one forecaster over the whole of the forecast period. These projections provide an indication of what is, in our view most likely to happen, not what it will definitely happen.
Short- and medium-term forecasts are based on a “demand-side” forecasting framework, under the assumption that supply adjusts to meet demand either directly through changes in output or through the depletion of inventories.
Long-term projections rely on a supply-side framework, in which output is determined by the availability of labour and capital equipment and the growth in productivity.
Long-term growth prospects, are impacted by factors including the workforce capabilities, the openness of the economy to trade, the legal framework, fiscal policy, the degree of government regulation.
Direct contribution to GDP
The method for calculating the direct contribution of an industry to GDP, is to measure its ‘gross value added’ (GVA); that is, to calculate the difference between the industry’s total pretax revenue and its total boughtin costs (costs excluding wages and salaries).
Forecasts of GDP growth: GDP = CN+IN+GS+NEX
GDP growth estimates take into account:

Market Quantification
All relevant markets are quantified utilizing revenue figures for the forecast period. The Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) within each segment is used to measure growth and to extrapolate data when figures are not publicly available.
Revenues
Our market segments reflect major categories and subcategories of the global market, followed by an analysis of statistical data covering national spending and international trade relations and patterns. Market values reflect revenues paid by the final customer / end user to vendors and service providers either directly or through distribution channels, excluding VAT. Local currencies are converted to USD using the yearly average exchange rates of local currencies to the USD for the respective year as provided by the IMF World Economic Outlook Database.
Industry Life Cycle Market Phase
Market phase is determined using factors in the Industry Life Cycle model. The adapted market phase definitions are as follows:

The Global Economic Model
The Global Economic Model brings together macroeconomic and sectoral forecasts for quantifying the key relationships.
The model is a hybrid statistical model that uses macroeconomic variables and inter-industry linkages to forecast sectoral output. The model is used to forecast not just output, but prices, wages, employment and investment. The principal variables driving the industry model are the components of final demand, which directly or indirectly determine the demand facing each industry. However, other macroeconomic assumptions — in particular exchange rates, as well as world commodity prices — also enter into the equation, as well as other industry specific factors that have been or are expected to impact.
Forecasts of GDP growth per capita based on these factors can then be combined with demographic projections to give forecasts for overall GDP growth.
Wherever possible, publicly available data from official sources are used for the latest available year. Qualitative indicators are normalised (on the basis of: Normalised x = (x - Min(x)) / (Max(x) - Min(x)) where Min(x) and Max(x) are, the lowest and highest values for any given indicator respectively) and then aggregated across categories to enable an overall comparison. The normalised value is then transformed into a positive number on a scale of 0 to 100. The weighting assigned to each indicator can be changed to reflect different assumptions about their relative importance.

The principal explanatory variable in each industry’s output equation is the Total Demand variable, encompassing exogenous macroeconomic assumptions, consumer spending and investment, and intermediate demand for goods and services by sectors of the economy for use as inputs in the production of their own goods and services.
Elasticities
Elasticity measures the response of one economic variable to a change in another economic variable, whether the good or service is demanded as an input into a final product or whether it is the final product, and provides insight into the proportional impact of different economic actions and policy decisions.
Demand elasticities measure the change in the quantity demanded of a particular good or service as a result of changes to other economic variables, such as its own price, the price of competing or complementary goods and services, income levels, taxes.
Demand elasticities can be influenced by several factors. Each of these factors, along with the specific characteristics of the product, will interact to determine its overall responsiveness of demand to changes in prices and incomes.
The individual characteristics of a good or service will have an impact, but there are also a number of general factors that will typically affect the sensitivity of demand, such as the availability of substitutes, whereby the elasticity is typically higher the greater the number of available substitutes, as consumers can easily switch between different products.
The degree of necessity. Luxury products and habit forming ones, typically have a higher elasticity.
Proportion of the budget consumed by the item. Products that consume a large portion of the
consumer’s budget tend to have greater elasticity.
Elasticities tend to be greater over the long run because consumers have more time to adjust their behaviour.
Finally, if the product or service is an input into a final product then the price elasticity will depend on the price elasticity of the final product, its cost share in the production costs, and the availability of substitutes for that good or service.
Prices
Prices are also forecast using an input-output framework. Input costs have two components; labour costs are driven by wages, while intermediate costs are computed as an input-output weighted aggregate of input sectors’ prices. Employment is a function of output and real sectoral wages, that are forecast as a function of whole economy growth in wages. Investment is forecast as a function of output and aggregate level business investment.





 Industry: Services and Business Services
Industry: Services and Business Services